|
|
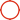
In the electroplating process, carriers (also often referred to as electroplating carriers or hanger auxiliary carriers) are functional components used in conjunction with hangers. Their core role is to optimize the stability, uniformity, and production efficiency of the electroplating process. Their specific functions can be divided into the following categories:
1.Improving the uniformity of current distribution For workpieces with complex shapes, deep holes, grooves, or edges and corners, direct electroplating is prone to problems such as current concentration at the edges and corners (resulting in burning and burrs) and insufficient current in the depressions (thin plating or missing plating). Carriers can act as auxiliary electrodes or shielding parts to adjust the electric field distribution, allowing the current to cover the workpiece surface more uniformly, ensuring consistent plating thickness and stable quality.
2.Carrying small-sized or light and thin workpieces For tiny parts (such as electronic connector pins, precision hardware) or light, thin, and easily deformable workpieces that cannot be directly fixed on hangers, carriers can provide dense hanging points or holding slots to fix multiple small workpieces in an orderly manner. This avoids collision and stacking of workpieces during electroplating and ensures that each workpiece is in full contact with the electroplating solution.
3. Reducing hanger loss and improving utilization Carriers can serve as a buffer layer between hangers and workpieces, reducing direct contact wear between workpieces and hangers, and extending the service life of hangers. At the same time, one carrier can carry multiple workpieces, significantly increasing the loading capacity of a single electroplating operation and improving production efficiency.
4.Improving the convection and contact of the electroplating solution Some carriers are designed with diversion holes or specific structures, which can promote the flow of the electroplating solution on the workpiece surface, avoid local concentration polarization, ensure uniform deposition of metal ions, and reduce defects such as pinholes and pitting.
5.Adapting to automated production lines In automated electroplating processes, standardized carriers can be accurately matched with the fixtures and transmission equipment of the production line, realizing automatic loading, electroplating, and unloading of workpieces, and improving the degree of automation and consistency of production.
It should be noted that the material of the carrier needs to be selected according to the electroplating system. Usually, materials that are resistant to acid and alkali and have good conductivity (such as titanium alloy, stainless steel, and conductive plastic) are chosen to prevent the carrier itself from being corroded or affecting the plating composition.
Contact Person: Ms. Emily Chan
Tel: 86-0-13006369714